FICARE MODEL AND STRUCTURE OF THE NICU
Departments and hospital information
Department information
Welcome to the neonatology department of University Teaching Hospitals-Women and Newborn Hospital.
The ward is an Open Bay Unit: there are several incubators and/or cribs in the same unit/room. The specialised nurses provide care for the infants. The workspace for the doctors and nursing staff has been placed in the middle of the ward. In this workspace, the nurses can oversee the monitors of the different babies, and the glass walls allow them to keep a close eye on the ward.
As soon as children are stable enough and don’t need high complex neonatal care anymore, they can sometimes be transferred to the Kangaroo Mother Care ward which is part of the neonatology department. The last bit of the hospital admission can then be completed in this department, where the nurses can support things such as learning how to feed, skin to skin contact and caring for your baby.
The Mothers Shelter is accommodation within the hospital premises for stable mothers with babies admitted to the NICU. Please speak to the staff if you need assistance with accommodation. In some cases, mothers may be admitted in the postnatal ward while caring for their baby in NICU. Stable mothers with babies admitted in the Kangaroo Mother Care ward can stay with their babies.
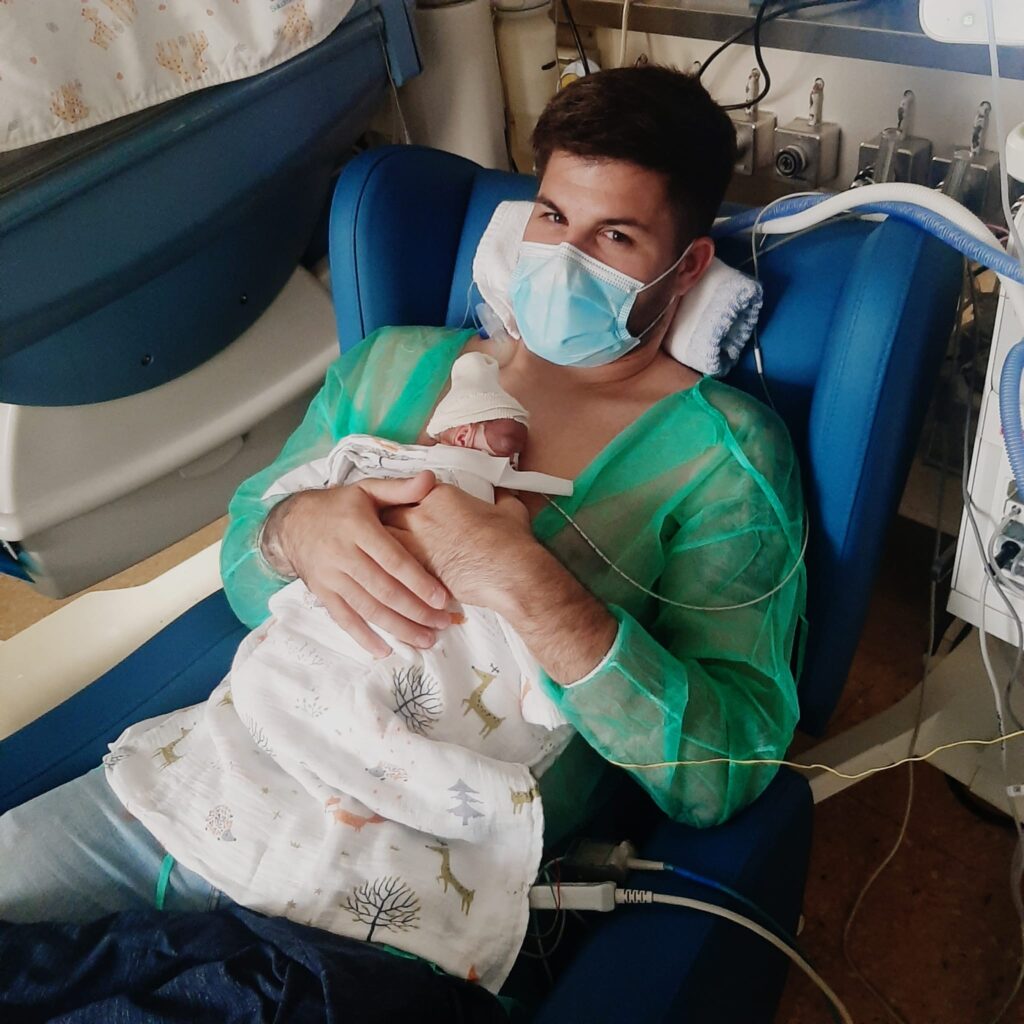
Visiting rules relatives and friends
In most departments of neonatology parents are welcome 24 hours a day, and in some wards such as the Kangaroo Mother Care, it is possible to stay with your baby throughout the day and night. Young children are not allowed on the unit. Visiting hours are between 06:00-07:00 and 16:00-17:00. Two visitors at a time may see your baby, one of them being a parent, and will require identification forms for security purposesChanging visitors is possible within limitations. Visitors who do not feel well or are ill, for instance, with a cold or cold sores, are not allowed to visit the department. If in doubt, please ask a nurse or other team member. In special situations these visiting rules change for the safety of the patient and the family. We ask you to store your belongings before entering the room or ward. Make sure not to leave any valuables behind. Before you enter the ward or the room, you have to wash your hands thoroughly (see also the article “Washing hands”).
Hospital facilities
For parking you can use the public parking available on the hospital premises. There are some eateries near the main building of the hospital and near the hospital. Meals are provided at no extra charge for parents/guardians staying in the Mothers Shelter or Kangaroo Mother Care ward.
Who is who
In the department of neonatology various disciplines are involved in your baby’s treatment. It is nice to know who you are dealing with during your baby’s stay in hospital.
Rooming-in during a stay in hospital
The Kangaroo Mother Care ward is the only ward under the department of neonatology that allows for stable babies, generally premature, to stay with their mothers whilst preparing to go home. It gives you the chance to look after your baby yourself with support from the nurses. You are supposed to do the feeding yourself. If you breastfeed, usually a breastfeeding plan is made in consultation with the nutritionist and/or nurse. Some babies will be able to be fed everything from the breast, while others are too tired for this. Babies get assessed daily for readiness for discharge home.